Overview
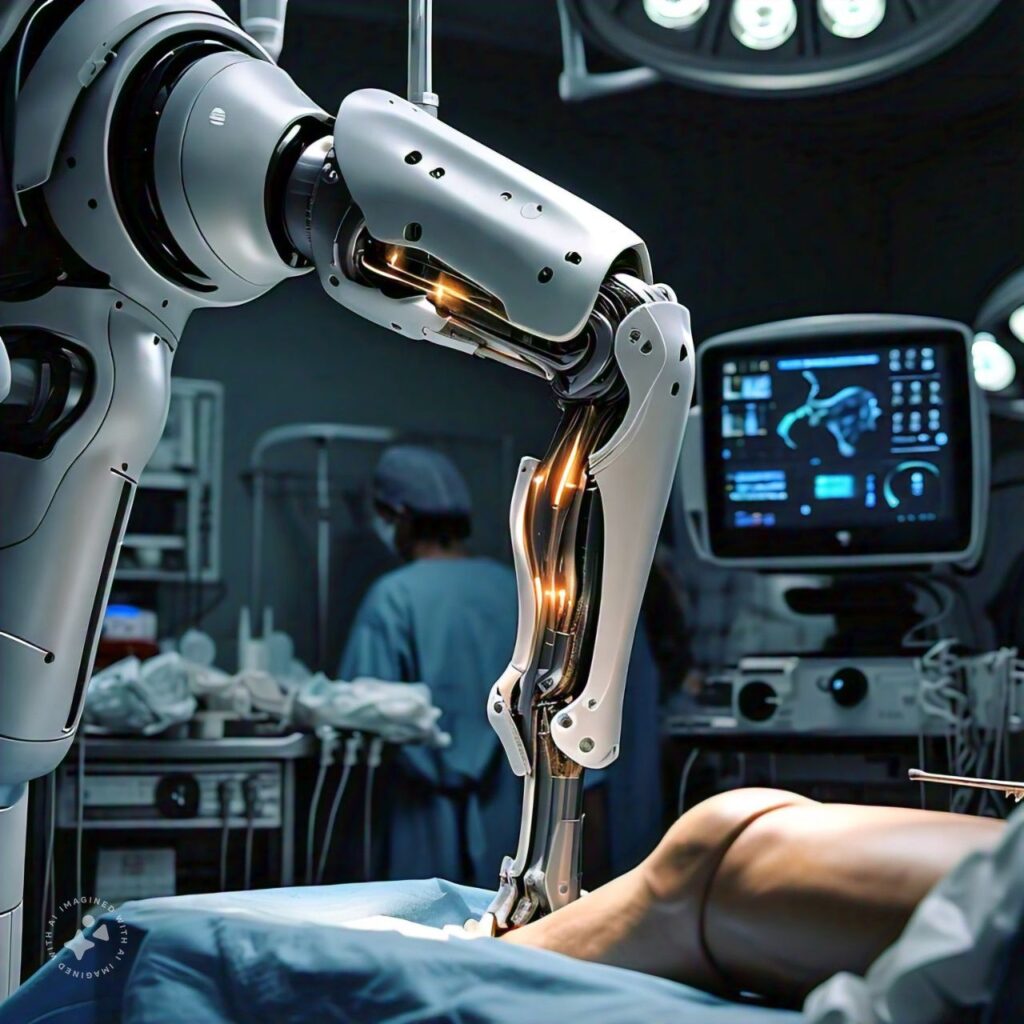
Robotic Knee Replacement
Robotic knee replacement is a modern surgical approach designed to enhance the accuracy and outcomes of knee replacement surgery. By integrating advanced robotic technology, this procedure aims to improve implant placement and patient satisfaction.
What is Robotic Knee Replacement?
Robotic knee replacement involves the use of robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing total or partial knee replacements. These systems utilize pre-operative imaging, such as CT scans or MRIs, to create a detailed 3D model of the patient’s knee. This model helps the surgeon in planning the procedure with precision, allowing for custom-tailored surgical strategies.

Benefits of Robotic Knee Replacement
- Precision and Accuracy: Robotic systems enhance the precision of bone cuts and implant positioning, potentially leading to better alignment and joint function.
- Customization: Pre-operative planning allows for a patient-specific approach, accommodating individual anatomical variations.
- Reduced Soft Tissue Damage: The precision of robotic assistance can minimize damage to surrounding soft tissues, which may lead to quicker recovery times.
- Improved Recovery and Outcomes: Some studies indicate that robotic-assisted surgeries can result in improved early functional outcomes and patient satisfaction compared to traditional methods.
- Consistent Results: The use of robotics can increase the consistency of outcomes due to standardized and precise surgical techniques.
Considerations and Limitations
- Availability and Cost:
Robotic systems are costly and may not be available in all healthcare facilities. The cost of the procedure can also be higher than traditional knee replacement. - Surgeon Expertise:
The effectiveness of robotic knee replacement depends significantly on the surgeon’s experience and training with the robotic system. - Patient Suitability:
Not all patients may be suitable candidates for robotic knee replacement. Factors such as bone quality and overall health must be considered. - Surgical Time:
The procedure may take longer due to the additional planning and setup required for using robotic systems.
Conclusion
Robotic knee replacement represents a significant advancement in orthopedic surgery, offering potential benefits in terms of precision, personalized treatment, and improved recovery. However, it is essential for patients to engage in detailed discussions with their orthopedic surgeon to determine if this approach aligns with their specific needs and circumstances. As with any surgical procedure, individual evaluation and careful planning are crucial to achieving the best possible outcomes.